The world we live in is brimming with modern technology. You can’t go to a store without purchasing something that has undergone modernization. Over the past century, innovation has led to technological revolutions across various fields. If you are looking to set the pace with your business and provide leading edge services, it is essential to know who were the famous inventors of modern technology and how they changed the world forever.
Everyone knows about Bill Gates, Steve Jobs, and Mark Zuckerberg. But there were many others before them who had a significant impact on the lives we live today. What do you know about them?
Hedy Lamarr, inventor of signal hopping
Hedy Lamarr was a Hollywood star who became an inventor. In 1942, she and composer George Antheil came up with the idea for frequency hopping to help military submarines communicate during World War II.
Signal hopping is a technique for sending information securely. It involves switching communication frequencies between several different channels at short intervals. This makes it impossible for eavesdroppers to pick up any information being sent over those channels, because they can’t differentiate between real data and random noise.
Lamarr and Antheil received the first patent for this technology, and it became part of modern day Wi-Fi, GPS and Bluetooth.
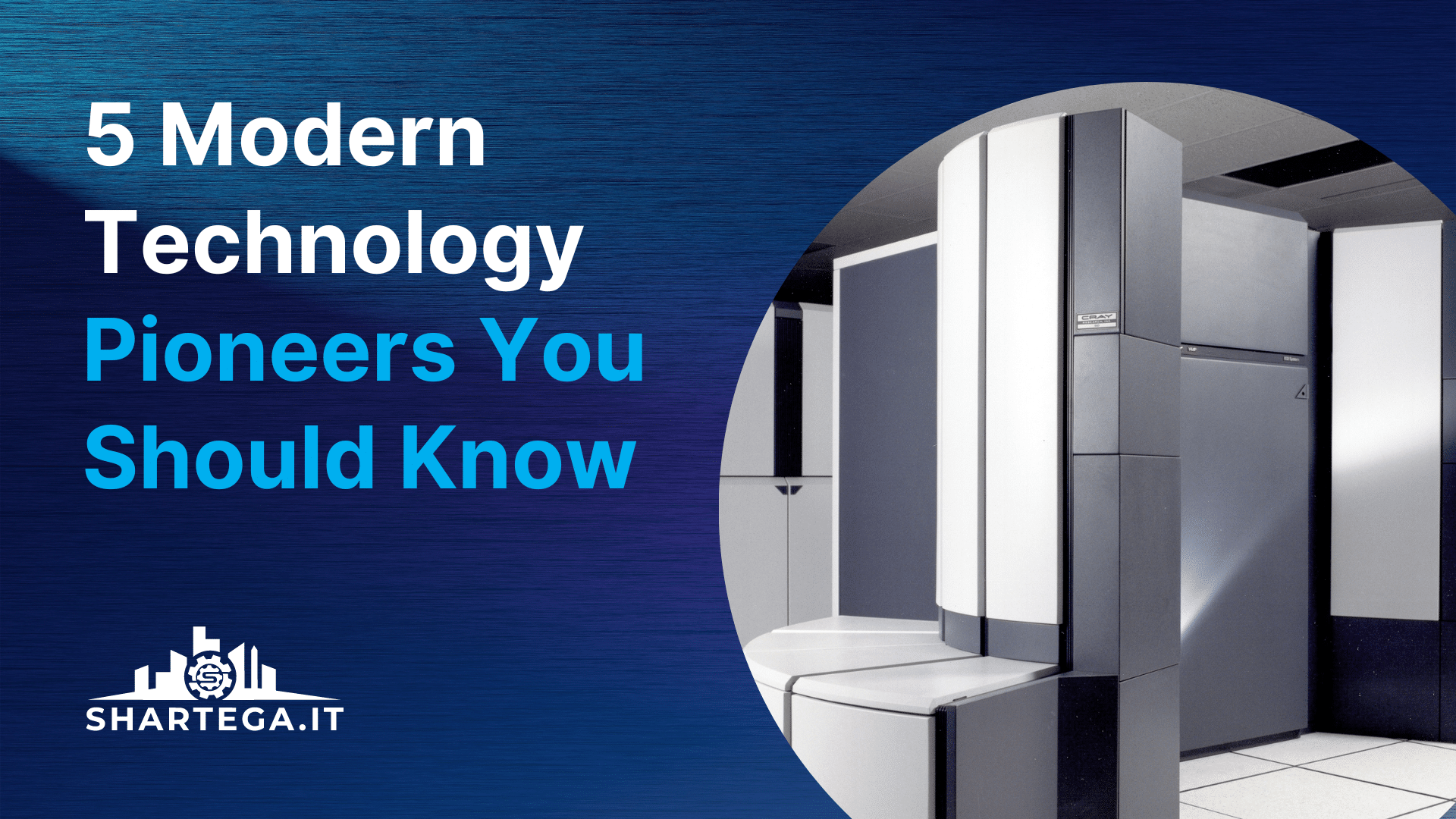
Seymour Cray, father of the supercomputer
Seymour Cray was a pioneer in computer technology, most notably for his work at Control Data Corporation (CDC). He is considered the father of supercomputing.
He made his name in the 1950s by designing the CDC 6600, a supercomputer that could perform up to 1.5 million instructions per second. This made it one of the fastest computers in the world at the time.
In 1972, Seymour Cray left Control Data Corporation (CDC) to form his own company, Cray Research. The Cray-1 was the first computer released by his company. It is known for its iconic cylindrical design and for being the fastest supercomputer throughout the mid-70s and early 80s.
Martin Cooper, pioneer of the cell phone
Martin Cooper was an engineer at Motorola when he was tasked with creating a mobile phone prototype for consumers. He came up with the DynaTAC 8000x, which weighed 2 pounds and could fit in a briefcase. It cost $3,995 and had 30 minutes of talk time before needing a recharge.
He made the first successful call with it on April 3, 1973, while standing on Sixth Avenue in New York City before a press conference. He called his competitor Joel Engel, who worked at AT&T, and told him that he was calling from a portable handheld phone.
Tim Berners-Lee, creator of the world wide web
Tim Berners-Lee is a British computer scientist and the inventor of the World Wide Web. He wrote the first proposal for what would become the World Wide Web in 1989. He implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and server via the Internet in mid-1991.
Berners-Lee wrote a paper in 1989 that described how to create a universal online information system. It included several key concepts that underpin today’s internet, such as:
Hyperlinks – The idea that each web page could link to any other web page so that users could navigate between them.
HTML – A simple way to mark up text with formatting instructions.
URLs – Uniform Resource Locators allowed you to specify the location of a resource on the web.
Berners-Lee is currently director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), an organization that he founded in 1994. The consortium provides technical standards and guidelines for developing web applications and services as well as overseeing the development of new technologies related to the web.
Larry Page and Sergey Brin, co-founders of Google
Google’s founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, were both students at Stanford University when they began working on the search engine in 1996. They initially called it “BackRub,” but later changed it to Google because of the mathematical term “googol” and because it was easy to pronounce.
Google’s search engine uses algorithms to analyze pages from all over the Web and then ranks them based on how relevant they are to the keywords you enter. The PageRank algorithm determines the ranking of results. If a page has a high ranking, it means that it has been linked to by other popular pages. Similarly, if a page has no links pointing to it, it will have a low PageRank score.
The company has since introduced several other services in addition to its search engine, such as Gmail in 2004, Google Maps in 2005, and Google Chrome in 2008.
Takeaway
Ultimately, the world of technology owes a great deal of gratitude to its founders. They have given us the ability to communicate with each other across the world, reach vast amounts of information in a fraction of a second and harness almost infinite amounts of energy—a privilege that was once strictly confined to science fiction.