We understand that data security is an essential aspect of any modern organization, regardless of its size or industry. As businesses continue to expand their digital footprint and customer base, the threat of cyber attacks looms larger than ever before. Therefore, it is critical to have a robust data security policy in place to protect customer data and safeguard your organization’s reputation.
In this article, we will discuss the must-have elements of a data security policy that will help you protect customer data and stay ahead of cyber threats. We will explore key concepts and strategies that will enable you to create a comprehensive data security policy that aligns data protection standards with your organization’s objectives and eliminates security concerns.
The Data Security Policy Explained
A data security policy is a comprehensive set of guidelines and procedures that an organization follows to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of its data. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of employees, the types of data that the data protection policy covers, and the measures that an organization takes to protect its data. A data security policy is an essential component of an organization’s overall security posture and helps to safeguard against data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other security threats.
There are various measures an organization can take to ensure data security, including encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software. These measures are designed to prevent unauthorized access company data, detect and respond to security incidents, and protect against malware and other cyber threats.

Key Elements of a Data Security Policy
Data Classification & Labeling
The first step in developing an effective data security policy is to identify and classify your organization’s data assets. This step involves determining the data stored, the sensitivity of the data, its value, and the level of access required to view and manipulate it. Once this is done, it is essential to label and categorize the data according to its level of confidentiality, so that appropriate security measures can be applied to personally identifiable information.
Access control and authentication
Access control is another critical element of data security. It involves controlling who has access to sensitive data and what level of access they have. This involves implementing multi-factor authentication protocols, which require users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing sensitive data.
Logical and physical security
Physical security refers to the physical measures taken to protect a physical location, equipment, or other tangible assets. Examples of physical security measures include security cameras, access controls, locks, barriers, and guards. Physical security is important for preventing unauthorized access, theft, damage, and other physical threats.
Logical security, on the other hand, refers to the digital measures taken to protect computer systems, networks, and data. Examples of logical security measures include firewalls, encryption, access controls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems. Logical security is important for preventing unauthorized access, data breaches, malware attacks, and other digital threats.
Encryption
Encryption is a crucial aspect of data security that involves encoding sensitive data so that it can only be accessed by authorized personnel. This process ensures that even if data is stolen, it cannot be used or read by unauthorized parties. There are different types of encryption methods, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption, which can be used depending on the sensitivity of the data being protected.
Incident response planning
It is important to have a plan in place in case of a data breach. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, including data breach notification procedures, how to isolate and contain the breach, and how to notify affected parties. Regular testing and updating of the plan is also essential to ensure its effectiveness.
Regular security assessments
Regular security assessments are essential to ensure that your organization’s data security policy is up-to-date and effective. These assessments should be conducted by a third-party security professional and should include vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and compliance audits. This step will ensure that your organization is well-prepared to deal with potential threats.
Steps to Creating a Data Security Policy
Creating a data protection and security policy involves several steps:
Determine the scope
The policy should clearly define the scope of the data security policy. This includes the types of data covered, the systems and devices involved, and the personnel responsible for enforcing the policy. The policy should also identify the legal and regulatory requirements that apply to the organization’s data protection activities.
Identify risks
A risk assessment should identify the potential risks associated with each type of data and the vulnerabilities in the organization’s systems and devices. This information will inform the security measures that the organization will implement. The risk assessment should be conducted regularly to ensure that the policy is up-to-date and effective.
Develop security measures
Based on the risk assessment, the organization should develop various security controls and measures to protect data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or destruction. These measures should include access controls, encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software. The organization should also establish procedures for incident response and data retention and disposal.
Implement the policy
The policy should be communicated to all personnel who handle data and implemented throughout the organization. This includes training personnel on the policy, conducting regular audits to ensure compliance, and enforcing the policy through disciplinary measures if necessary.
Maintain and update the policy
A data security policy should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that it remains effective in addressing new and emerging threats. This includes conducting regular risk assessments, testing the policy through simulations, and reviewing and updating the data security policy template, as necessary.
Creating a data security policy is an important step in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or destruction. By developing data security policies and following these steps, an organization can develop an effective data security policy that protects its data and reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks.

Mobile Devices in Data Security Policies
Mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, have become critical tools for businesses to stay connected and productive. However, with increased use comes increased risk, and it is essential to ensure that they are secure to protect sensitive business information.
Use business-grade mobile devices
One of the most important steps in securing mobile devices for business use is to use business-grade devices that come with built-in data security controls and features. These devices often include encryption, remote wipe, and mobile device management (MDM) tools that allow administrators to control and secure the devices remotely.
Implement a mobile device policy
A mobile device policy outlines the rules and procedures that employees must follow when using these devices for business purposes. The policy should include guidelines on password complexity, app usage, and data storage, as well as procedures for reporting lost or stolen devices.
Use an MDM solution
MDM solutions allow administrators to manage and secure mobile devices remotely. They can enforce security policies, such as password complexity and encryption, and monitor devices for security threats. MDM solutions can also provide real-time visibility into device usage and allow administrators to remotely wipe devices if necessary.
Train employees on mobile device security
Employees should be trained on the best practices for mobile device security, such as using strong passwords and avoiding unsecured Wi-Fi networks. They should also be aware of the potential risks of downloading apps or accessing sensitive information on unsecured devices.
Conduct regular security audits
Regular security audits can help identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure that mobile devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates. Audits can also identify unauthorized devices or apps that may pose a security risk.

Example Data Security Policy Template
The following is an example data security policy template that organizations can use as a starting point to create their own policy. This template is intended to be flexible and customizable to meet the specific needs of each organization.
Purpose
The purpose of this policy is to ensure that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access or data breaches. This policy outlines the rules and procedures that employees must follow to maintain the security of the organization’s data.
Scope
This policy applies to all employees, contractors, and third-party vendors who have access to the organization’s data.
Policy
- Access Control: Employees must use secure passwords and follow best practices for password management. Access to sensitive information should be restricted to only those employees who require it for their job.
- Data Handling: Sensitive information should be handled with care and only be accessed, copied, or transmitted as necessary. Employees should not store sensitive information on personal devices or cloud storage services.
- Incident Reporting: Employees should report any suspected security incidents or violations of this policy immediately to the IT department.
- Remote Access: Employees who access the organization’s data remotely must use secure connections and follow the same security protocols as if they were on the organization’s premises.
- Encryption: Sensitive information should be encrypted when transmitted or stored to prevent unauthorized access.
- Security Awareness: Employees should be trained on the policies and procedures outlined in this policy and any updates to the policy. Regular security awareness training should be conducted to ensure that employees understand their role in maintaining the security of the organization’s data.
Enforcement
Violations of this policy may result in disciplinary action, up to and including termination of employment. Any suspected criminal activity will be reported to the appropriate authorities.
Review and Revision
This policy will be reviewed and updated as needed to ensure that it remains relevant and effective in protecting the organization’s sensitive information.
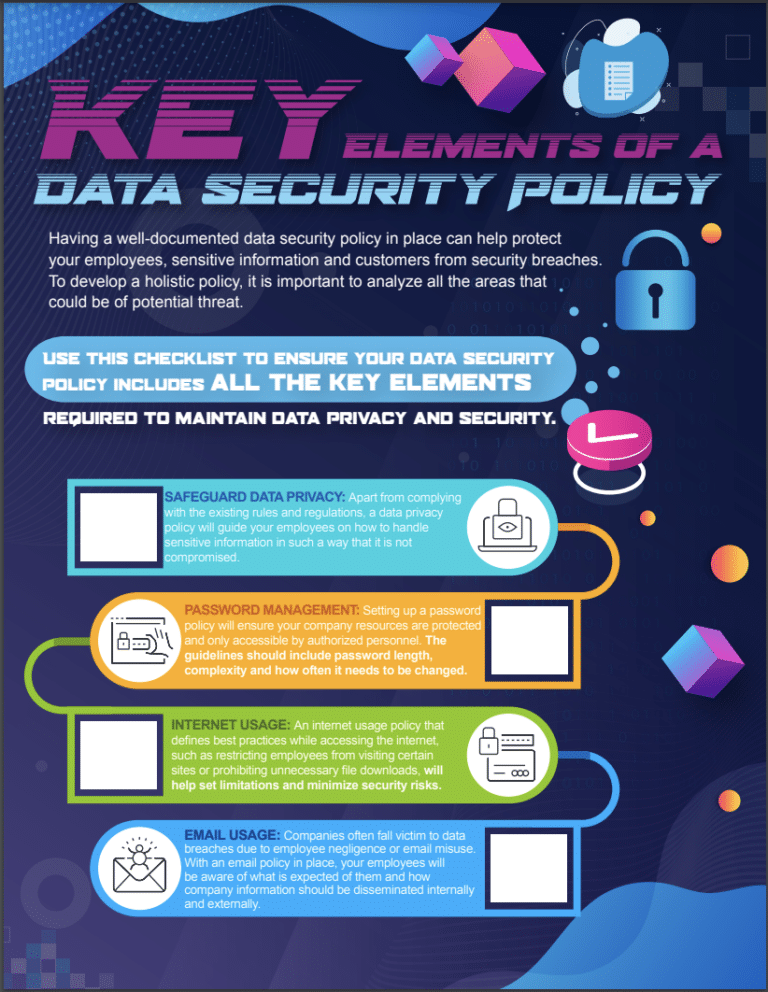
Download Our Data Security Checklist eBook
We’ve compiled a data security policy checklist so you can start crossing these essential items off your list and see where you currently stand with your policy.